
Savonia article: Nursing Insight – Addressing healthy eating and promoting healthy elderly
The global population has been experiencing gradual growth, especially the number of people aged 60 and above. In 2022, the old population stands at 5.5 million and is expected to be 1.0 to 1.5 billion individuals aged 65 and older by 2031, with the majority of women in Finland (Statistics Finland 2022). Therefore, it is important to consume a healthy diet to promote wellbeing and heathy aging. In this article, we will delve into strategies for both maintaining and promoting a healthy diet among Finnish elderly population.
The article aims to explain why it’s important for nurses to know about healthy eating for the elderly. It also explores how nurses can use this knowledge in their caregiving.
Promoting healthy eating among the elderly: A healthy diet supplies the necessary macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) to support physical activity and meet physiological needs. Macronutrients play an important role in providing energy, supporting growth, and enhancing the body’s immune system. Meanwhile, vitamins and minerals, although needed in smaller quantities, are essential for overall body development, metabolism, and tissue function. Nutritional needs vary significantly between elderly and their younger counterparts. Aging causes changes in the digestive system, which often lead to various digestive disorders in the elderly e.g. dysphagia, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation. (WHO 2023)
Finnish dietary guidelines for elderly people
In the plate model designed for elderly by the Finnish Nutrition Council (2014) (Figure), suggested that the plate be divided into thirds. One-third of the plate should be filled with cooked or fresh vegetables, another third with high-protein sources, and the final third filled with carbohydrate-rich foods. The fat free dairy products, cheese, yogurt, and fruit desserts are suitable choices as snacks. Additionally, a thin layer of soft vegetable spread on bread is also recommended in plate model. Vegetable oil and margarine not only provide essential vitamins A, D, and E but also provide high calories. (Valtion ravitsemusneuvottelukunta 2014)
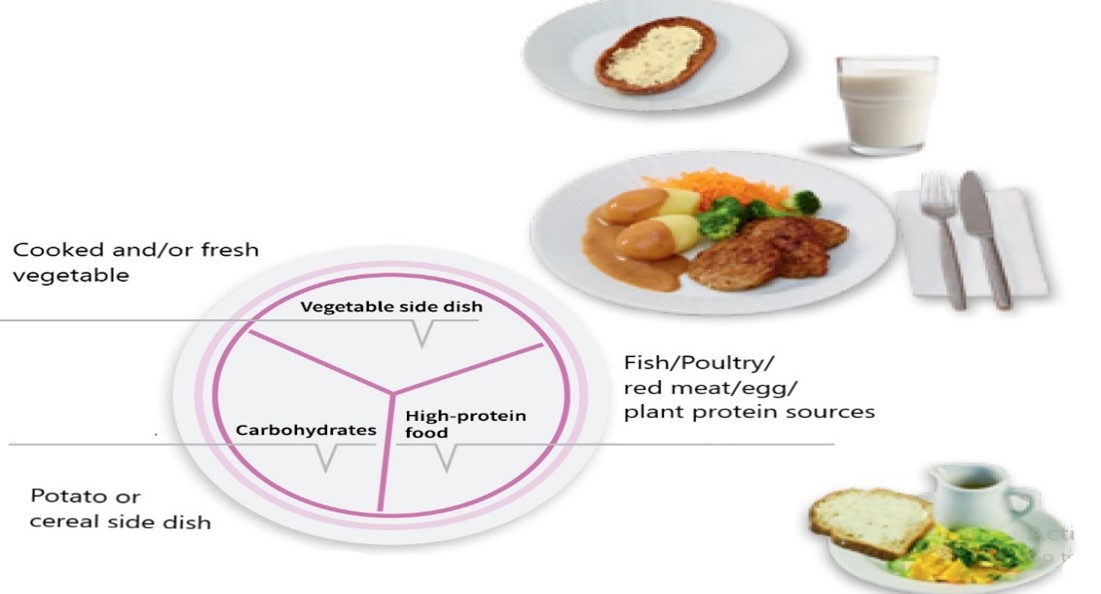
The sixth edition of the Nordic Nutritional Recommendations (NNR 2023) advises a shift towards a plant-based diet, encourages higher fish consumption, and recommends a reduction in meat intake. According to NNR, the protein consumption should be 1.2-1.5g/kg body weight. Weekly at least two-time fish consumption is also recommended. Fish is a good source of vitamins A, B, D, and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids which have positive impact on healthy aging and prevent cardiovascular diseases. Water intake should be 2.0L/day and 2.5L/day is for female and male. (NNR 2023)
Importance of healthy eating for elderly people
The well-being of elderly is influenced by several factors such as daily food intake, physical condition, the duration of illnesses, social factors, and medication. Among these factors, nutrition holds a particularly vital role. As both the quality and quantity of consumed food have an impact on the well-being and quality of life of elderly. Daily dietary intake significantly affects their physical and cognitive health, bone strength, and immune system resilience during the later stages of life. Additionally, healthy food consumption can prevent gastrointestinal disorders, non-communicable diseases, for example diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, and nutrition deficiency malnutrition. Proper nutrition supports a strong immune system, helping the body defend against infections and reduce the risk of cognitive decline like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. A balanced diet can positively impact the mental health, prevent depression and anxiety, which are common among the elderly. (Granic et al. 2020)
Role of nurses to promoting healthy eating among the elderly
Nurses are the primary healthcare service providers who are responsible for assessing the health condition of elderly. Therefore, the implementation of a balanced diet in nursing care setting is mostly dependent on the nurses for preserving their patient’s health and overall well-being.
Nurses are first tier care giver for the elderly, they may use standardized nutritional screening tools to quickly identify individuals at risk of malnutrition or other dietary concerns. Nurses assess the specific nutritional needs and dietary preferences of each elderly patient considering factors such as age, gender, weight, medical history, and any specific dietary restrictions or preferences. (Ernstmeyer & Christman, 2021) The names of the tools are- Mini Nutrition Assessment (MNA), the Malnutrition Screening Tool (MST), and the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (‘MUST’). (Donini et al. 2016).
Steps of nutritional assessments:
Height, Weight, and Body Mass Index (BMI): Nurses measure the individual’s weight and height to calculate their BMI, which provides insights into their nutritional status. Significant changes in weight can indicate nutritional issues.
Dietary History: Nurses gather information about the elderly person’s typical dietary intake. This includes asking about meal patterns, dietary restrictions, allergies, smoking and alcohol consumption.
Clinical Evaluation: Nurses examine the physical appearance of elderly person, including signs of malnutrition, muscle wasting, fat loss and dehydration or edema. Nurses review the person’s medical history, including chronic conditions, medications, and any recent surgeries that may impact their nutritional needs.
Functional Assessment: Nurses evaluate the individual’s ability to perform activities of daily living, including the ability to shop for groceries, cook, and feed themselves. Functional limitations can affect their dietary choices and access to food. (Everitt, Davies, & Omori, 2023)
Implication of nutrition education for the nurses
As the nurses are primarily response for overall wellbeing and caregiver for the elderly, it is important that nurses get evidence-based nutrition knowledge and training related to education to implement those in health care setting:
Nutrition Education: Nurses must have adequate understanding of the nutritional needs of the elderly, including how aging can affect nutrient absorption, metabolism, and the risk of certain health conditions.
Special Diets: They should be knowledgeable about various dietary restrictions and special diets, such as low-sodium, diabetic, or dysphagia diets. Understanding food safety is important to prevent foodborne illnesses, which can be more severe in older adults.
Communication and Collaboration: Nurses communicate their findings with the healthcare team, including dietitians, physicians, and other specialists. This collaborative approach ensures that the elderly person receives appropriate nutritional care. (Amoey et al 2017)
In conclusion, old age represents a particularly vulnerable stage of life as elderly people are more susceptible to different types of illnesses. However, nurses can play an important role in facilitating the adoption of a healthy dietary lifestyle in preventing these diseases and promoting healthy aging.
Author:
Saima Kamal Thakur, Registered Nurse, Bachelor of Health Care, Savonia University of Applied Sciences, Kuopio, Finland